Monday, September 22, 2008
Friday, September 12, 2008
3rd grade: History of the World - #1c creation and the beginning of time
When God moves his law is applied to all things. His law defined time. When he moved he started time. This was the beginning of History.
God moved, resonance, and when he moved, with his plan and law, and started time so many things happened!
BBC Skillswise has nice lessons, games and worksheets on time:
12-hour and 24-hour time
- am is morning time (all times between 12 midnight and
12 midday). - pm is afternoon and evening time (all times between 12
midday and 12 midnight). - This is an analogue or a 12-hour clock. An analogue clock
is one with a face and hands. It is showing the time
twenty past five.
If it were twenty past five in the morning, it would
be written as 5:20 am.
If it were twenty past five in the afternoon, it would
be written as 5:20 pm. - These are digital or 24-hour clocks. They are also
showing the times twenty past five.
- The 24-hour time is the same as the analogue time in the
morning (except for the 0 at the beginning for numbers
under 10). So 8:45 am becomes 08:45. - But in the afternoon, you need to add 12 to convert an
analogue time to a 24-hour time. So 8.45 pm
becomes 20.45. - Midday on a 24-hour clock is shown as 12:00.
- Midnight on a 24-hour clock is shown as 00:00.
- 1 minute = 60 seconds
- 1 hour = 60 minutes
- 1 day = 24 hours
- 1 week = 7 days
- 1 fortnight = 14 days
- 1 year = 12 months = 52 weeks = 365 days
- 1 leap year = 366 days
- Remember "30 days has September, April, June and
November. All the rest have 31. Except for February
alone, which has 28 days clear but 29 each leap year."
Genesis 1
1In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth.
2And the earth was without form, and void; and darkness was upon the face of the deep. And the Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters.
3And God said, Let there be light: and there was light.
4And God saw the light, that it was good: and God divided the light from the darkness.
5And God called the light Day, and the darkness he called Night. And the evening and the morning were the first day.
Wednesday, September 10, 2008
Monday, September 8, 2008
3rd grade: History of the World - #1e creation and the beginning of time
Forces and Motion
These lessons are about forces and motion. It has these parts in it:
To work out the speed of an object, we need to know two things:
- the distance it has traveled
- the time taken to travel that distance.
There are two common situations:
| Situation | Fastest object |
| Two objects travel the same distance in different times | The one that takes the shortest time |
| Two objects travel different distances in the same time | The one that travels the longest distance |
This is the equation for working out speed:
Genesis 1
Friday, September 5, 2008
3rd grade: History of the World - #1d creation forces in action
When God moved, resonance and time started, law came to all things and so many things happened. When he moved he made energy.
Energy Resources and Energy Transfer
BBC Schools: Energy basicsEnergy allows things to happen. If you leap around wildly, people often say that you have lots of energy. Energy allows you to move around and keep warm. It allows you to see and to hear. Energy cannot be created out of thin air or destroyed - it can only be stored or transferred from place to place in different ways. Let's look at some examples.

The vibrating drum and the plucked guitar string transfer energy to the air as sound. This sound energy can be transferred to your eardrum as kinetic energy (movement energy).

The battery transfers stored chemical energy as electrical energy in the moving charges in the wires. The electrical energy is transferred to the surroundings by the lamp as light energy and thermal energy (heat energy).

The rock on the mountain has stored energy because of its position above the ground and the pull of gravity. This energy is called gravitational potential energy. As the rock falls to the ground, the gravitational potential energy is transferred as kinetic energy.

A cup of hot tea has heat energy in the form of kinetic energy from its particles. Some of this energy is transferred to the particles in cold milk, which you pour in to make the tea cooler.

When the explosive goes off, chemical energy stored in it is transferred to the surroundings as thermal energy, sound energy and kinetic energy.
- Energy transfer diagrams
- Temperature and heat
- Transfer of thermal energy
- Non-renewable energy resources
- Renewable energy resources
- Saving energy
Genesis 1
1In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth.
2And the earth was without form, and void; and darkness was upon the face of the deep. And the Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters.
3And God said, Let there be light: and there was light.
4And God saw the light, that it was good: and God divided the light from the darkness.
5And God called the light Day, and the darkness he called Night. And the evening and the morning were the first day.
3rd grade: History of the World - #1b creation forces in action
God created the heaven and the earth. They were created before they were. When it was dark and void God had the plan. He is the light to lighten the dark. God is the law to validate the void. He is the source of all the forces, the source from above! He is the "Heavy Weight" of all mass. He gives weight, length, and capacity to all things.
BBC has nice lessons, games and worksheets HERE.
Forces in action
1. Gravity
- The force that makes things fall to the ground on Earth is called gravity.
- Gravity also holds Earth and the other planets in their orbits around the Sun.
- The force of gravity also exists on the moon but it is not as strong as it is on the Earth (this is because the moon is much smaller than the Earth).

2. Mass and weight
- The mass of an object is how much matter it contains. It is measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg) but is NOT a force.
- The weight of an object is the force caused by gravity pulling down on the mass of an object. It is measured in Newtons (N).
- Weight is measured using a forcemeter. The bigger the weight attached to the forcemeter, the more the spring inside the forcemeter stretches.

3. Balanced forces
- Forces are just pushes and pulls in a particular direction.
- Forces are shown by arrows in diagrams. The direction of the arrow shows the direction in which the force is acting. The bigger the arrow, the bigger the force.
- If two forces are balanced, it means the forces are the same size but are acting in opposite directions.
- If two balanced forces are acting on an object, that object will not change its motion. If it is still, it will stay still. If it is moving, it will continue moving, in the same direction and at the same speed.

4. Unbalanced forces
- Unbalanced forces can make objects start to move, speed up, slow down, or change direction.

Genesis 1
1In the beginning God created the heaven and the earth.
2And the earth was without form, and void; and darkness was upon the face of the deep. And the Spirit of God moved upon the face of the waters.
3And God said, Let there be light: and there was light.
4And God saw the light, that it was good: and God divided the light from the darkness.
5And God called the light Day, and the darkness he called Night. And the evening and the morning were the first day.
Thursday, September 4, 2008
3rd grade: History of the World - #6a creation
The 6th day of the World
God made living creatures on the dry land of the earth. He made them mature in order to multiply.
Moving and growingWhat Came First, the Chicken or the Egg?
by John D. Morris PhD
This age-old question really has a simple answer. Attempts to answer it, however, and attempts to get around implications of the simple answer are often quite convoluted.
According to the Creator of chickens, and the author of the Record of their origins, chickens came first. It was on the Fifth Day of Creation Week that He created "every winged fowl after [their] kind" (Genesis 1:21) complete with the DNA to reproduce that kind. Then He "blessed them, saying, Be fruitful, and multiply" (v.22) using that DNA. For the chickens this meant lay chicken eggs. Problem solved.
Read the rest HERE.
1. Skeletons and muscles
- Many animals have skeletons to support and protect their body and to help it move.


- The human skeleton is made of bone and grows as we grow. Our skull protects our brain and our ribs protect our heart and lungs.

- The skeleton bends at joints such as knees and ankles. Joints are where two or more bones join together.
- Muscles are attached to bones. When a muscle contracts (squashes up), it gets shorter and so pulls up the bone it is attached to. When a muscle relaxes, it goes back to its normal size. This is how skeletons move.

- Some animals, such as insects, crabs and lobsters, have a skeleton outside their body. Such skeletons are called exoskeletons.

2. Human life cycle

Genesis 1
25And God made the beast of the earth after his kind, and cattle after their kind, and every thing that creepeth upon the earth after his kind: and God saw that it was good.
3rd grade: History of the World - #5 creation
The 5th day of the World
God made living creatures in the waters.

God made flying creatures above the earth.
It was good.
Variation
1. Grouping living things
- Plants and animals can be divided into groups by looking at the similarities and differences between them.
- Plants are divided into two groups, flowering plants and non-flowering plants.
- Animals are divided into two main groups. Animals that have a backbone are called vertebrates. Animals that don't have a backbone are called invertebrates.
- Vertebrates and invertebrates are divided into smaller groups. Vertebrates, for example, are divided into mammals, birds, amphibians, fish and reptiles.

2. Keys
- A key is just a series of questions about the characteristics of living things.
- You can use a key to identify a living thing or decide which group it belongs to by answering the questions.
- Here is an example of a key. You can use the key to identify each of these animals.


Genesis 1
20And God said, Let the waters bring forth abundantly the moving creature that hath life, and fowl that may fly above the earth in the open firmament of heaven.
21And God created great whales, and every living creature that moveth, which the waters brought forth abundantly, after their kind, and every winged fowl after his kind: and God saw that it was good.
22And God blessed them, saying, Be fruitful, and multiply, and fill the waters in the seas, and let fowl multiply in the earth.
23And the evening and the morning were the fifth day.
3rd grade: History of the World - #4 creation
God made lights for signs, and for seasons, and for days, and years.
God made two great lights.
The sun rules the day.
The moon rules the night.
It was good.
Earth, Sun and Moon
1. The Earth
- The Earth is roughly spherical, like a slightly squashed ball.
- The Earth travels around the Sun once every year.
- The Earth also spins on its own axis (an imaginary line through its centre) once every 24 hours. This causes day and night on Earth. On the part of the Earth that is facing the sun, it is day; on the part of the Earth that is facing away from the sun, it is night.

2. The moon
- The moon is roughly spherical and is a lot smaller than the Earth.
- The moon travels around the Earth once every 28 days.
- We only see the part of the moon that is lit by the Sun. So sometimes we see the whole Moon and sometimes we only see part of the Moon.

3. The sun
- The sun is a star and gives out heat and light.
- It is roughly spherical in shape and is much, much bigger than the Earth.
- The Earth is just one of eight planets that travel around the sun. The other planets are called Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.

Genesis 1
15And let them be for lights in the firmament of the heaven to give light upon the earth: and it was so.
16And God made two great lights; the greater light to rule the day, and the lesser light to rule the night: he made the stars also.
17And God set them in the firmament of the heaven to give light upon the earth,
18And to rule over the day and over the night, and to divide the light from the darkness: and God saw that it was good.
19And the evening and the morning were the fourth day.
3rd grade: History of the World - #3 creation
The 3rd day of the world
God made grass, herbs, and trees with seeds.
It was good.
Helping plants grow well
1. What a plant needs to grow
- A plant needs air, light, warmth, water and nutrients to grow well.
- A healthy plant is upright with green leaves.

- A seed will not produce a plant at all if it is kept too cold. The seed needs warmth to germinate and start to grow into a healthy plant.

- A plant that is kept in a dark place will grow tall and spindly in search of light and then become weak and die.

- A plant that is not watered will have a weak stem and dried up leaves and will eventually die.

2. What different parts of plants do
- The roots of a plant take up water and nutrients from the soil. The roots also keep the plant steady and upright in the soil; they "anchor" the plant.
- The stem carries water and nutrients to different parts of the plant.
- The leaves use light from the sun, along with carbon dioxide from the air and water to make food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.

Genesis 1
11And God said, Let the earth bring forth grass, the herb yielding seed, and the fruit tree yielding fruit after his kind, whose seed is in itself, upon the earth: and it was so.
12And the earth brought forth grass, and herb yielding seed after his kind, and the tree yielding fruit, whose seed was in itself, after his kind: and God saw that it was good.
13And the evening and the morning were the third day.
3rd grade: History of the World - #2 creation
God made the Heaven. God made the water.
God made the Earth. God made the Seas.
It was good.
Changing state
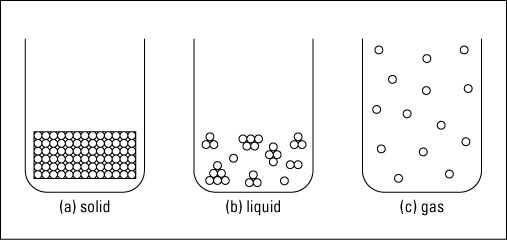
1. States of matter- Nearly everything exists as solids, liquids or gases. Solids, liquids and gases are called the three states of matter.
- Materials can be changed from one state to another by heating or cooling.
- If ice (solid) is heated, it changes to water (liquid). This change is called melting.
- If water (liquid) is heated, it changes to water vapour (gas). This change is called evaporation.
- If water vapour (gas) is cooled, it changes to water (liquid). This change is called condensing.
- If water (liquid) is cooled, it changes to ice (solid). This change is called freezing.

2. The water cycle
Water on the earth is constantly moving. It is recycled over and over again. This recycling process is called the water cycle.

The sun heats up water on land, and in rivers, lakes and seas and turns it into water vapour. The water vapour rises into the air.
b. Water vapour condenses into clouds
Water vapour in the air cools down and changes back into tiny drops of liquid water, forming clouds.
c. Water falls as rain
The clouds get heavy and water falls back to the earth in the form of rain or snow.
d. Water returns to the sea
Rain water runs over the land and collects in lakes or rivers, which take it back to the sea. The cycle starts all over again.
Pass out Worksheet #1. Read together and discuss.
Pass out Worksheet #2. Complete Worksheet #2 from memory.
Genesis 1
6And God said, Let there be a firmament in the midst of the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters.
7And God made the firmament, and divided the waters which were under the firmament from the waters which were above the firmament: and it was so.
8And God called the firmament Heaven. And the evening and the morning were the second day.
9And God said, Let the waters under the heaven be gathered together unto one place, and let the dry land appear: and it was so.
10And God called the dry land Earth; and the gathering together of the waters called he Seas: and God saw that it was good.
3rd grade: History of the World - #1a creation day 1
 Lesson 1 - day 1
Lesson 1 - day 1God was. God is. God will be.
Genesis 1
Monday, September 1, 2008
#20 Hundred Years War 17: Patay
#1 The Hundred Years War
#2 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part One
#3 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part Two
#4 Hundred Years War 3: Sluys and Morlaix
#5 Hundred Years War 4: Caen
#6 The Hundred Years War 5: Crecy
#7 Hundred Years War 6: Calais
#8 Hundred Years War 7: Poitiers part 1
#9 Hundred Years War 7: Poiters part 2
#10 Hundred Years War 8: Treaty of Bretigny
#11 Hundred Years War 9: Henry V
#12 Hundred Years War 10: Harfluer
#13 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part one
#14 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part two
#15 Hundred Years War 12: The Treaty of Troyes
#16 Hundred Years War 13: Bauge and Meaux
#17 Hundred Years War 14: Verneuil
#18 Hundred Years War 15: Rouvray
#19 Hundred Years War 16: Orleans
#20 Hundred Years War 17: Patay
#19 Hundred Years War 16: Orleans
Part Two:
#1 The Hundred Years War
#2 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part One
#3 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part Two
#4 Hundred Years War 3: Sluys and Morlaix
#5 Hundred Years War 4: Caen
#6 The Hundred Years War 5: Crecy
#7 Hundred Years War 6: Calais
#8 Hundred Years War 7: Poitiers part 1
#9 Hundred Years War 7: Poiters part 2
#10 Hundred Years War 8: Treaty of Bretigny
#11 Hundred Years War 9: Henry V
#12 Hundred Years War 10: Harfluer
#13 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part one
#14 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part two
#15 Hundred Years War 12: The Treaty of Troyes
#16 Hundred Years War 13: Bauge and Meaux
#17 Hundred Years War 14: Verneuil
#18 Hundred Years War 15: Rouvray
#20 Hundred Years War 17: Patay
#18 Hundred Years War 15: Rouvray
#1 The Hundred Years War
#2 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part One
#3 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part Two
#4 Hundred Years War 3: Sluys and Morlaix
#5 Hundred Years War 4: Caen
#6 The Hundred Years War 5: Crecy
#7 Hundred Years War 6: Calais
#8 Hundred Years War 7: Poitiers part 1
#9 Hundred Years War 7: Poiters part 2
#10 Hundred Years War 8: Treaty of Bretigny
#11 Hundred Years War 9: Henry V
#12 Hundred Years War 10: Harfluer
#13 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part one
#14 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part two
#15 Hundred Years War 12: The Treaty of Troyes
#16 Hundred Years War 13: Bauge and Meaux
#17 Hundred Years War 14: Verneuil
#19 Hundred Years War 16: Orleans
#20 Hundred Years War 17: Patay
#17 Hundred Years War 14: Verneuil
#1 The Hundred Years War
#2 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part One
#3 Hundred Years War: Weapons Part Two
#4 Hundred Years War 3: Sluys and Morlaix
#5 Hundred Years War 4: Caen
#6 The Hundred Years War 5: Crecy
#7 Hundred Years War 6: Calais
#8 Hundred Years War 7: Poitiers part 1
#9 Hundred Years War 7: Poiters part 2
#10 Hundred Years War 8: Treaty of Bretigny
#11 Hundred Years War 9: Henry V
#12 Hundred Years War 10: Harfluer
#13 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part one
#14 Hundred Years War 11: Agincourt part two
#15 Hundred Years War 12: The Treaty of Troyes
#16 Hundred Years War 13: Bauge and Meaux
#18 Hundred Years War 15: Rouvray
#19 Hundred Years War 16: Orleans
#20 Hundred Years War 17: Patay
This blog is a work in progress. Come back often to see updates!
History Lessons
-
▼
2008
(47)
-
▼
September
(17)
- Planets and Stars
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #1c creation and...
- Noah: 2348 BC - Deluge
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #1e creation and...
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #1d creation for...
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #1b creation for...
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #6a creation
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #5 creation
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #4 creation
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #3 creation
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #2 creation
- 3rd grade: History of the World - #1a creation day 1
- European Map...
- #20 Hundred Years War 17: Patay
- #19 Hundred Years War 16: Orleans
- #18 Hundred Years War 15: Rouvray
- #17 Hundred Years War 14: Verneuil
-
▼
September
(17)